Commodity Codes Explained: Your Business's Global Trade Compliance
Commodity codes are pivotal elements within the international trade ecosystem, serving as the foundation for the classification of goods across global borders. These numerical identifiers are not merely bureaucratic tools, but key to navigating the complexities of tariffs, trade policies, and customs regulations.
When you are trading goods internationally, you must provide the appropriate commodity code for each item being shipped. This code determines the applicable trade tariff, duties and taxes, VAT, and other trade regulations that will impact the movement of your goods. It is essential to accurately identify and utilize the correct commodity code to avoid potential delays, penalties, or even seizure of goods by customs authorities.
What are Commodity Codes?
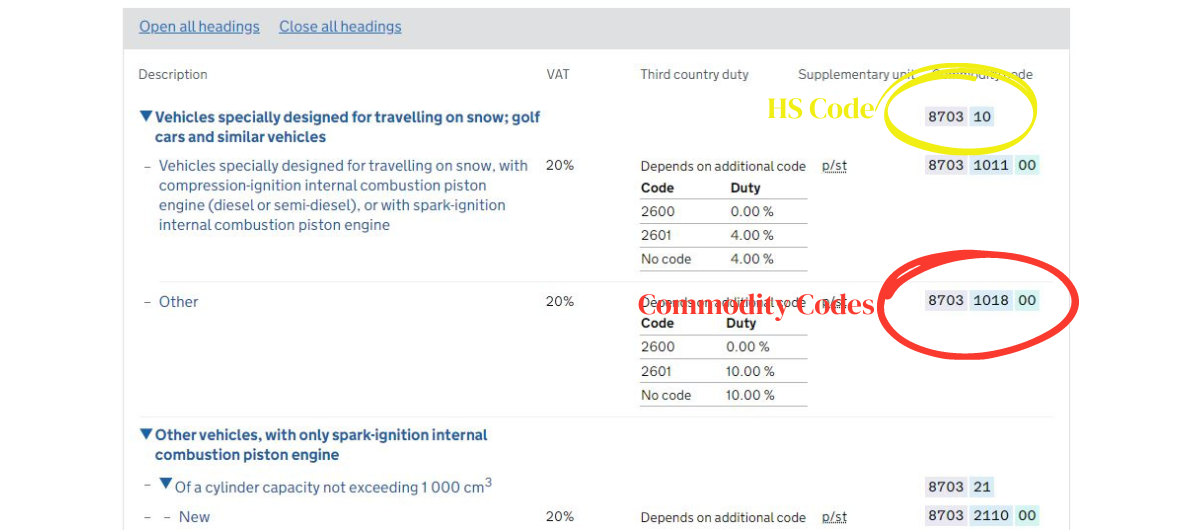
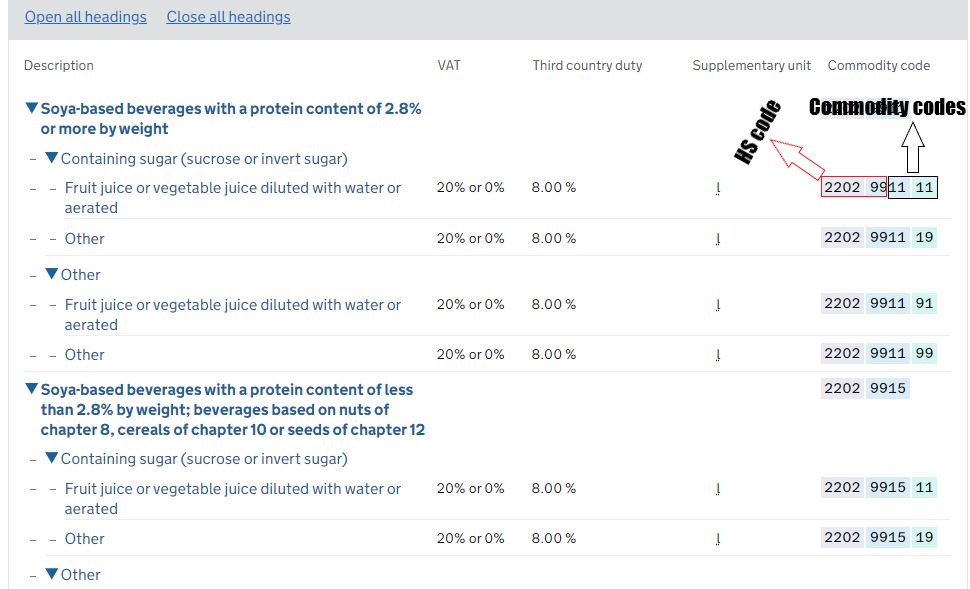
If you understand HS code, then you have a basic understanding of commodity codes. The HS code consists of six digits and is used to classify goods at an international level. However, commodity codes go beyond the HS code and are typically more detailed, with additional digits or letters added to further specify the type of product being traded.
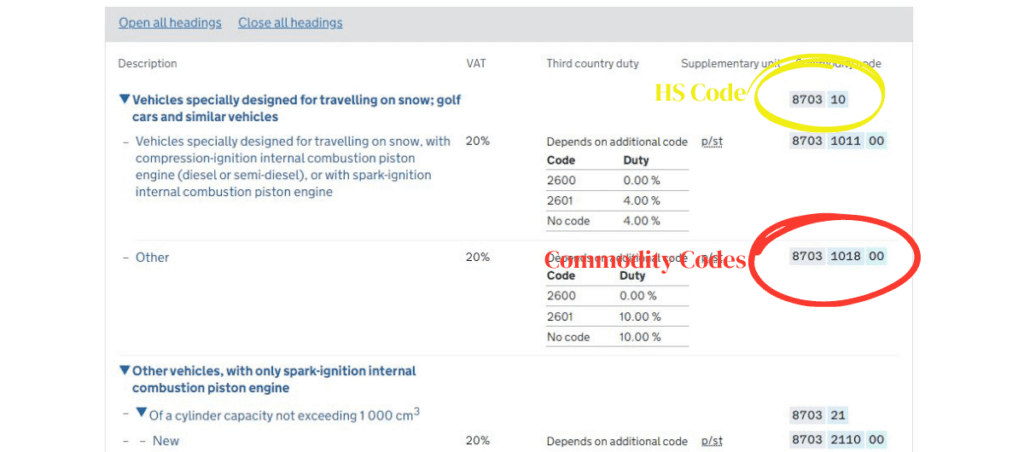
Together, commodity codes provide detailed information about the product, including its nature, composition, VAT, trade duty rates, and any applicable restrictions or regulations. This information is important for customs authorities to properly assess the goods being imported or exported.
How do you find your commodity codes?
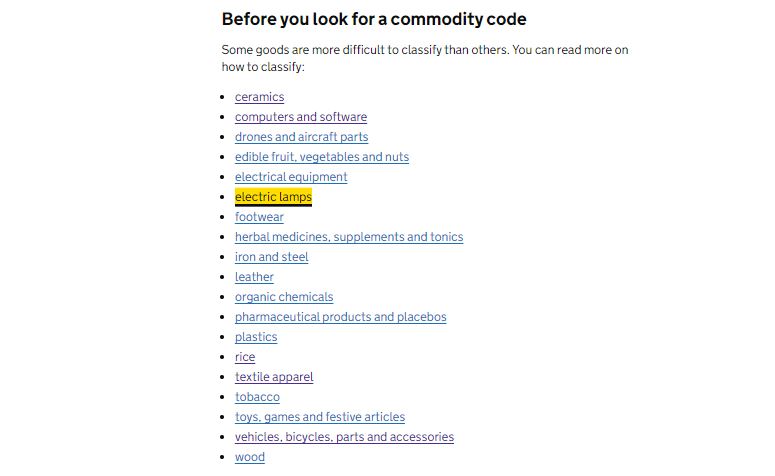
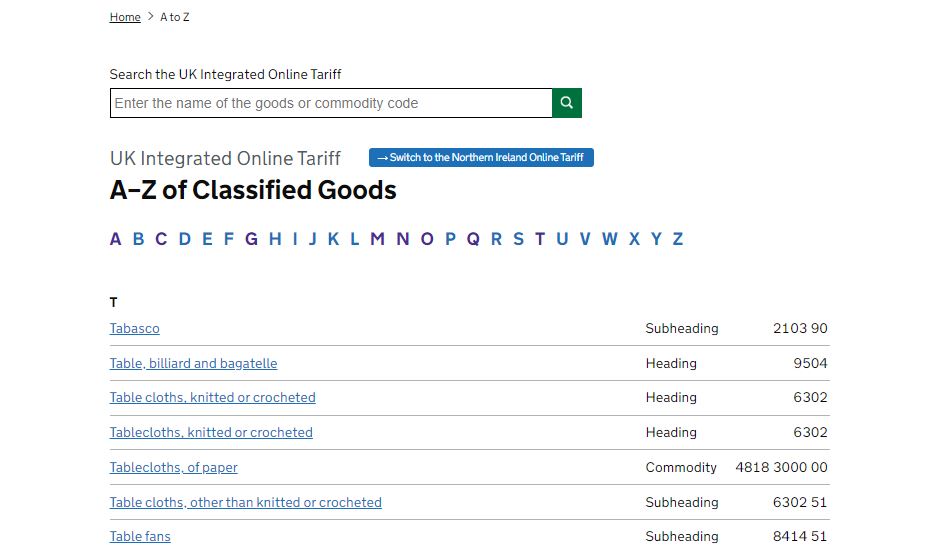
The UK Government has a comprehensive list of commodity codes that can be accessed through their website or through trade associations. You can get commodity codes by entering the product name at “A to Z of classified goods” or you simply check the “guidance on hard to classify goods” to get commodity codes for complex or unique products.
Sum Up:
As you can see, commodity codes are vital for international trade. That’s why it’s essential to accurately determine and utilize the correct commodity code for each product you are trading. If you’re struggling to find the appropriate code, be sure to consult with trade associations or customs clearance agents for guidance.
Recent Blog
-
Understanding Commodity Codes for Trading Success: A Comprehensive Guide
-
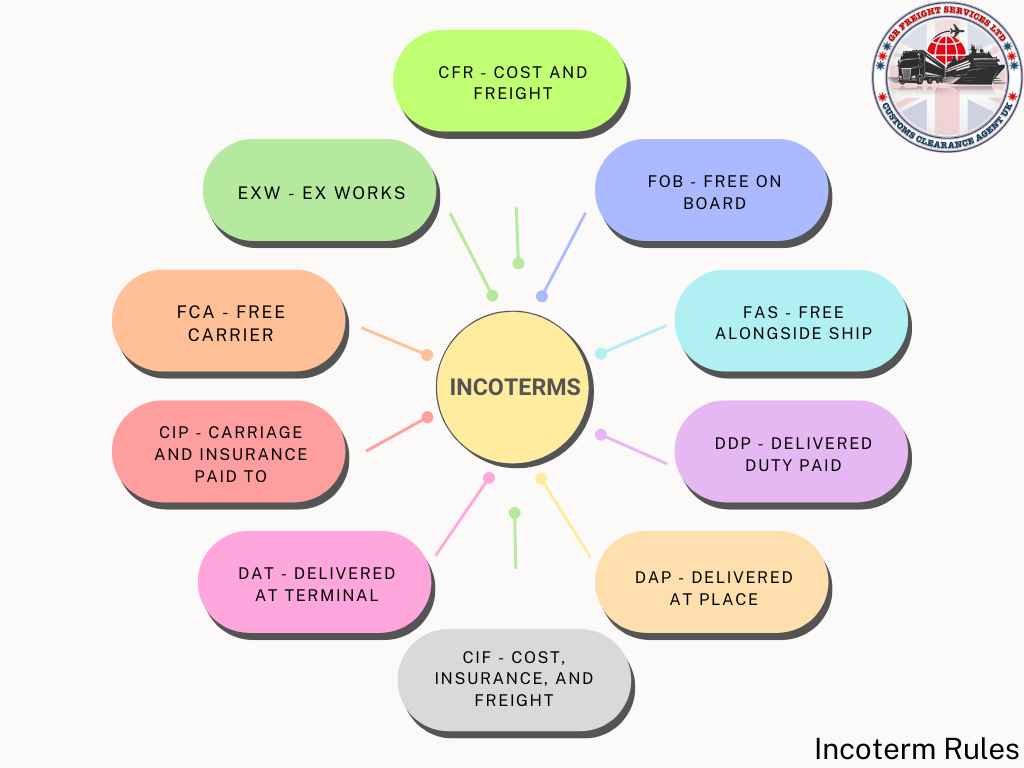
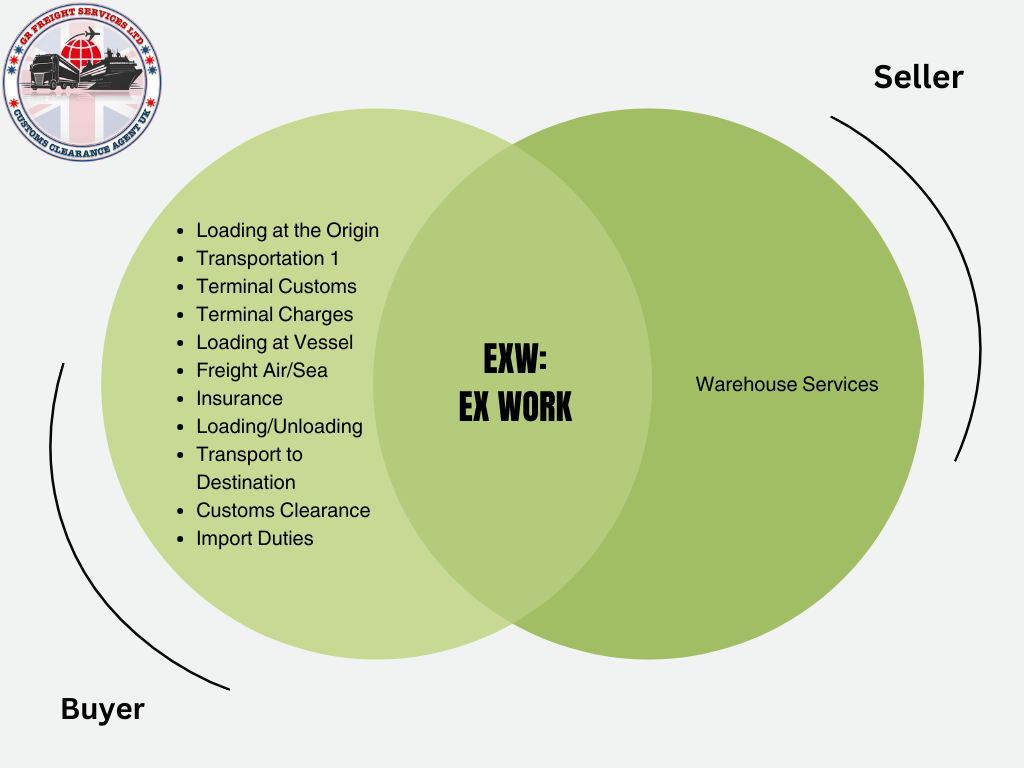
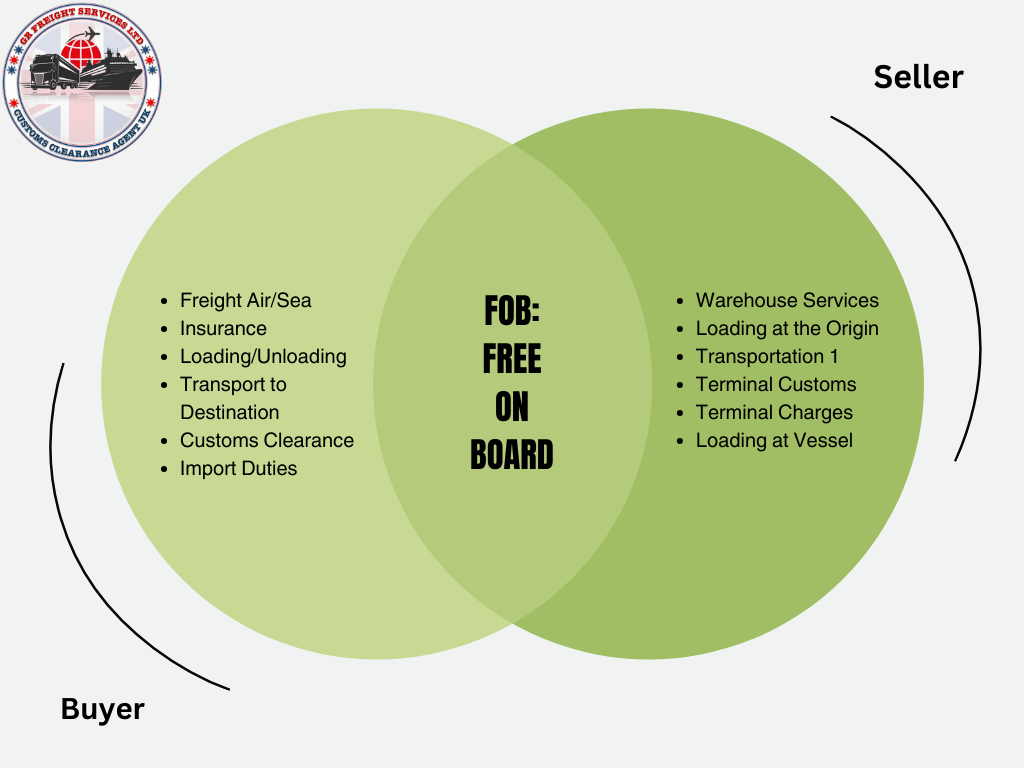
The Definitive Guide to Incoterms for Global Trading Partners
-
The Importance of Harmonized System (HS) Codes in Global Trade
-
Ultimate Guide: Import Mangoes to UK from Pakistan | Mango Import Process Explained
-
Fast Customs Clearance Services at Harwich Port – Get Cleared Today!